Application
Types of Pumps and
Their Applications in Industry

WHAT IS PUMP?
A pump is a device for converting the energy held by mechanical energy into hydraulic energy.
Function
-
Flow from a region of low pressure to one of high pressure
-
Flow from a low level to a higher level
-
Flow at a faster rate.
Properties
-
Flow from a region of low pressure to one of high pressure
-
Flow from a low level to a higher level
-
Flow at a faster rate.
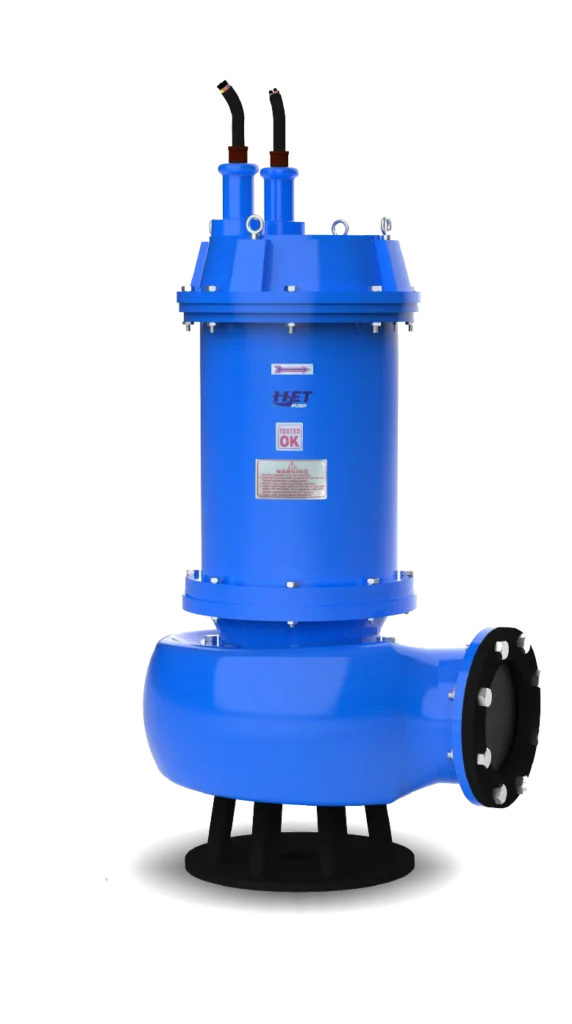
Single Stage PUMP
At Het Pump, we offer single stage submersible pumps designed for simplicity and performance. These pumps feature a single impeller that effectively transfers water or fluids in various applications, ensuring reliability and efficiency.
Key Features
-
Energy-efficient with low power consumption and high performance
-
Durable construction using corrosion-resistant materials for longevity
-
Easy installation with a simple design for hassle-free setup and maintenance
-
Versatile applications including residential, agricultural, and industrial use
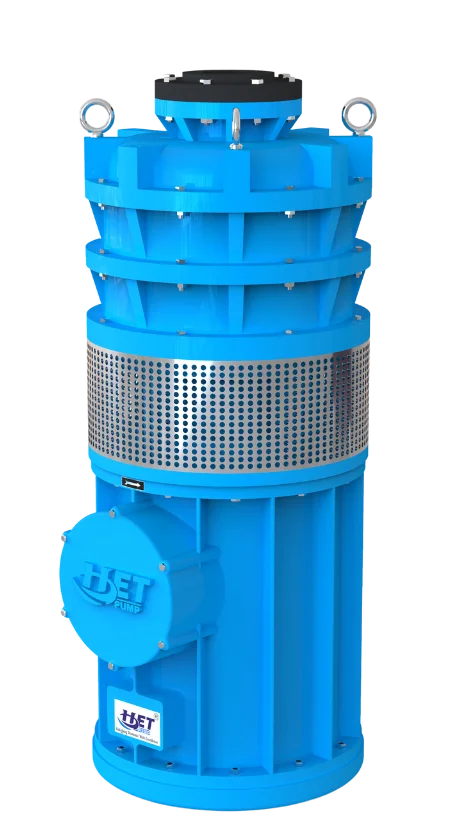


Multi Stage PUMP
Our double and multi-stage submersible pumps are designed for situations requiring high-pressure water transfer across long distances. With multiple impellers, these pumps deliver increased water pressure and are ideal for applications where a single stage pump might not suffice.
Key Features
-
High pressure output for efficient water transfer over long distances
-
Durable construction with premium materials for tough environments
-
Energy-efficient design optimized for high performance with low energy use
-
Versatile applications including industrial, agricultural, and municipal water systems

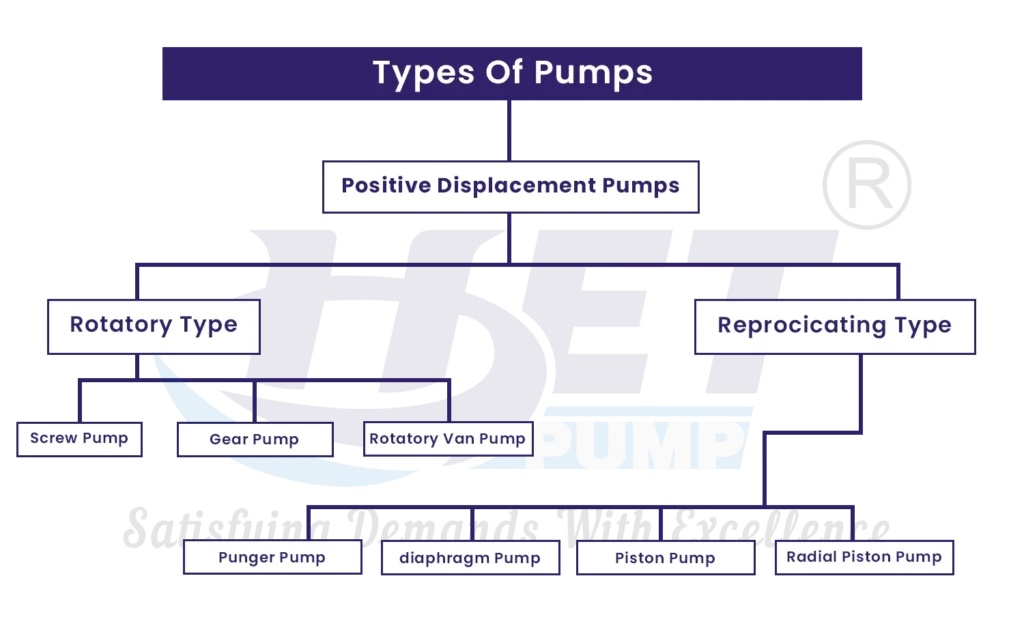
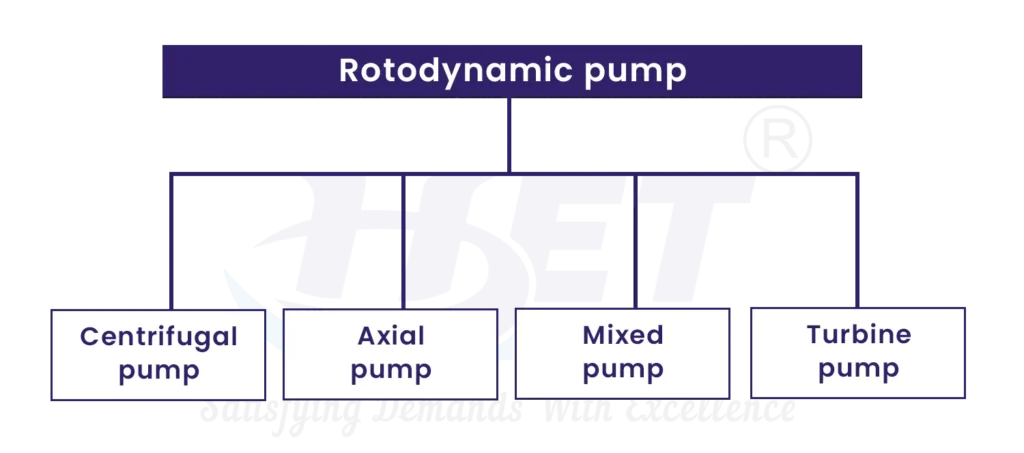
Types of Rotodynamic Pumps
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow.
Application
-
In power plants, pumps are crucial for circulating water from various sources to cool main condensers.
-
In the chemical industry, they facilitate the circulation of large liquid volumes in processes like evaporation and crystallization.
-
In sewage treatment facilities, Air Flotation Pumps (AFPs) enable effective internal recirculation of mixed liquor for optimal treatment.
-
In agriculture, high-capacity AFPs are used to lift water efficiently for irrigation and drainage.
-
In fisheries, pumps enhance operational efficiency by providing necessary water supply for various fishery processes.
These are also referred to as All fluid pumps. The fluid is pushed outward or inward and move fluid axially. They operate at much lower pressures and higher flow rates than radial-flow (centripetal) pumps.
Application
-
In power plants, pumps are essential for pumping water from various sources to cool main condensers.
-
In the chemical industry, pumps facilitate the circulation of large volumes of liquid in processes like evaporation and crystallization.
-
In sewage treatment facilities, Air Flotation Pumps (AFPs) ensure effective internal recirculation of mixed liquor for treatment.
-
In agriculture, high-capacity AFPs are used to lift water efficiently for irrigation and drainage.
-
In fisheries, pumps enhance operational efficiency by providing necessary water supply for fishery processes.
Mixed-flow pumps function as a compromise between radial and axial-flow pumps.
Application
-
In mixed-flow pumps, the design operates with an exit angle between 0 to 90 degrees, combining features of both axial-flow and radial-flow pumps.
-
They generate higher pressures compared to axial-flow pumps, making them suitable for applications requiring significant head.
-
Mixed-flow pumps deliver higher discharge rates than radial-flow pumps, making them ideal for transporting large volumes of fluid efficiently.
-
These pumps are commonly used in municipal water supply systems, where a balance of pressure and flow rate is essential.
-
They also find applications in irrigation and industrial processes, ensuring effective fluid transport.
